Terminology
The terms speech, language and communication are frequently used within school settings and by Speech and Language Therapists, however, the meaning of each term can sometimes become confused. These terms are frequently used to describe children’s difficulties and need to be understood in order to identify appropriate strategies for supporting them.
Speech
Speech refers to the physical production of sounds that we use to build up words, phrases and sentences. To achieve clear speech, we need to be able to say sounds accurately and in the correct places in words.
Language
Language is the term used for the words (vocabulary), grammar and sentences that we understand and how we organise them to communicate. Language ability is both receptive (understanding what others say) and expressive (what we ourselves use). Children’s receptive language ability is usually in advance of their expressive language ability, for example a one year old will be able to understand many words that are said to them, but they will be able to say very little. This continues as children get older, as they need to understand a word, concept or sentence structure, before they will be able to use it.
Communication
Communication is the way that we use language to interact with other people. We need to be able to use language in different ways and for different functions including to comment, inform, question, explain and reason. We need to understand the non-verbal rules of communication, such as facial expressions and body language. We also need to understand the social rules of language including taking turns and adapting our use of language to suit different situations. Communication can apply to information that is conveyed with words (spoken or written), noises, facial expressions or gestures and signs.
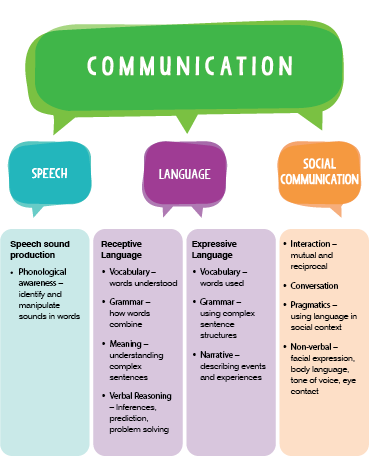
Speech
Speech sound production
Phonological awareness –identify and manipulate sounds in words
Language
Receptive Language
- Vocabulary – words understood
- Grammar – how words combine
- Meaning – understanding complex sentences
- Verbal Reasoning – Inferences, prediction, problem solving
Expressive Language
- Vocabulary – words used
- Grammar – using complex sentence structures
- Narrative – describing events and experiences
Social Communication
- Interaction – mutual and reciprocal
- Conversation
- Pragmatics – using language in social context
- Non-verbal – facial expression, body language, tone of voice, eye contact
Please login to view this content
Login